Section outline
-
LECTURES N. 13, 14, 17 and 18
lecture 18 was devoted to the setup of a project on the comparison of the dynamical structure of native and mutated viral lysozymes
initial conditions, integration schemes, force fields, integration schemes, thermostats
biological energy scales/biological time scales/ timescales of protein motions
protein folding in vivo (crowding) / in vitro
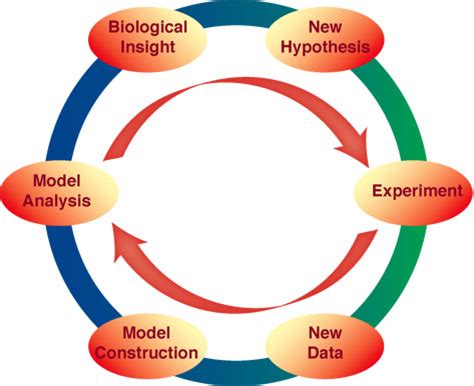
free energy barriers control relaxation times
protein disorder/protein order in the simulation (solid-like vs liquid-like motions)
quantum mechanics vs Molecular Mechanics
force fields: bonded + nonbonded parametrisation (see also lecture N. 3)
energy minimisation and the protein folding problem (recent application of AI: ALPHA FOLD 2)
typical observables in a protein MD simulation: RMSD(t), RMSF(t), Rg(t)
structural superposition of proteins
the problem of roto-translation subtraction
symplectic integrators, Verlet's algorithm: remarks on the Liouville’s formulation of the discretized dynamics
(Tsai2004, Binder_Ciccotti1996.pdf, Schiller2008)
Trotter product formula of operators
CONTROLLING TEMPERATURE AND PRESSURE IN MD
MD as generator of thermodynamical statistics, overview
Liouville formulation of the MD, factorization
Ensembles
Constant temperature MD: quenches, Anderson Thermostat, Nosè-Hoover Thermostat
Temperature Echo
CB_23_24_PACK_7
-